Description
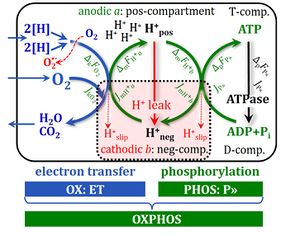
![]() The P-L net OXPHOS capacity is the OXPHOS capacity corrected for LEAK respiration. P-L is the scope for ADP stimulation, the respiratory capacity potentially available for phosphorylation of ADP to ATP. Oxygen consumption in the OXPHOS state, therefore, is partitioned into P-L, strictly coupled to phosphorylation P», and nonphosphorylating LEAK respiration, LP, compensating for proton leaks, slip and cation cycling: P = P-L+LP. It is frequently assumed that LEAK respiration L as measured in the LEAK state, overestimates the LEAK component of respiration, LP, as measured in the OXPHOS state, particularly if the protonmotive force is not adjusted to equivalent levels in L and LP. However, if the LEAK component increases with enzyme turnover during P, the low enzyme turnover during L may counteract the effect of the higher pmF.
The P-L net OXPHOS capacity is the OXPHOS capacity corrected for LEAK respiration. P-L is the scope for ADP stimulation, the respiratory capacity potentially available for phosphorylation of ADP to ATP. Oxygen consumption in the OXPHOS state, therefore, is partitioned into P-L, strictly coupled to phosphorylation P», and nonphosphorylating LEAK respiration, LP, compensating for proton leaks, slip and cation cycling: P = P-L+LP. It is frequently assumed that LEAK respiration L as measured in the LEAK state, overestimates the LEAK component of respiration, LP, as measured in the OXPHOS state, particularly if the protonmotive force is not adjusted to equivalent levels in L and LP. However, if the LEAK component increases with enzyme turnover during P, the low enzyme turnover during L may counteract the effect of the higher pmF.
Abbreviation: P-L
Reference: Gnaiger 2020 BEC MitoPathways
Communicated by Gnaiger E (2014-08-09) last update 2020-11-11
Keywords
- Expand Bioblast links to P-L net OXPHOS capacity
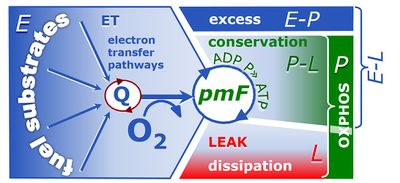
4-compartmental OXPHOS model. (1) ET capacity E of the noncoupled electron transfer system ETS. OXPHOS capacity P is partitioned into (2) the dissipative LEAK component L, and (3) ADP-stimulated P-L net OXPHOS capacity. (4) If P-L is kinetically limited by a low capacity of the phosphorylation system to utilize the protonmotive force pmF, then the apparent E-P excess capacity is available to drive coupled processes other than phosphorylation P» (ADP to ATP) without competing with P».
- Bioblast links: Coupling control - >>>>>>> - Click on [Expand] or [Collapse] - >>>>>>>
1. Mitochondrial and cellular respiratory rates in coupling-control states
| Respiratory rate | Defining relations | Icon | |
|---|---|---|---|
| OXPHOS capacity | P = P´-Rox | mt-preparations | |
| ROUTINE respiration | R = R´-Rox | living cells | |
| ET capacity | E = E´-Rox | » Level flow | |
| » Noncoupled respiration - Uncoupler | |||
| LEAK respiration | L = L´-Rox | » Static head | |
| » LEAK state with ATP | |||
| » LEAK state with oligomycin | |||
| » LEAK state without adenylates | |||
| Residual oxygen consumption Rox | L = L´-Rox |
2. Flux control ratios related to coupling in mt-preparations and living cells
| FCR | Definition | Icon | |
|---|---|---|---|
| L/P coupling-control ratio | L/P | » Respiratory acceptor control ratio, RCR = P/L | |
| L/R coupling-control ratio | L/R | ||
| L/E coupling-control ratio | L/E | » Uncoupling-control ratio, UCR = E/L (ambiguous) | |
| P/E control ratio | P/E | ||
| R/E control ratio | R/E | » Uncoupling-control ratio, UCR = E/L | |
| net P/E control ratio | (P-L)/E | ||
| net R/E control ratio | (R-L)/E |
3. Net, excess, and reserve capacities of respiration
| Respiratory net rate | Definition | Icon |
|---|---|---|
| P-L net OXPHOS capacity | P-L | |
| R-L net ROUTINE capacity | R-L | |
| E-L net ET capacity | E-L | |
| E-P excess capacity | E-P | |
| E-R reserve capacity | E-R |
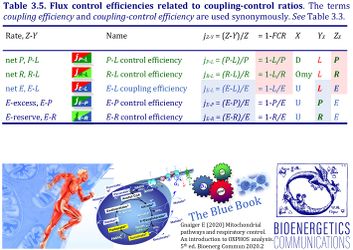
4. Flux control efficiencies related to coupling-control ratios
| Coupling-control efficiency | Definition | Icon | Canonical term | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P-L control efficiency | jP-L | = (P-L)/P | = 1-L/P | P-L OXPHOS-flux control efficiency | |
| R-L control efficiency | jR-L | = (R-L)/R | = 1-L/R | R-L ROUTINE-flux control efficiency | |
| E-L coupling efficiency | jE-L | = (E-L)/E | = 1-L/E | E-L ET-coupling efficiency » Biochemical coupling efficiency | |
| E-P control efficiency | jE-P | = (E-P)/E | = 1-P/E | E-P ET-excess flux control efficiency | |
| E-R control efficiency | jE-R | = (E-R)/E | = 1-R/E | E-R ET-reserve flux control efficiency |
5. General
- » Basal respiration
- » Cell ergometry
- » Dyscoupled respiration
- » Dyscoupling
- » Electron leak
- » Electron-transfer-pathway state
- » Hyphenation
- » Oxidative phosphorylation
- » Oxygen flow
- » Oxygen flux
- » Permeabilized cells
- » Phosphorylation system
- » Proton leak
- » Proton slip
- » Respiratory state
- » Uncoupling