Polyzos 2017 Mech Ageing Dev
| Polyzos AA, McMurray CT (2017) The chicken or the egg: mitochondrial dysfunction as a cause or consequence of toxicity in Huntington's disease. Mech Ageing Dev 161:181-97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mad.2016.09.003 |
Polyzos AA, McMurray CT (2017) Mech Ageing Dev
Abstract: Mitochondrial dysfunction and ensuing oxidative damage is typically thought to be a primary cause of Huntington's disease, Alzheimer's disease, and Parkinson disease. There is little doubt that mitochondria (MT) become defective as neurons die, yet whether MT defects are the primary cause or a detrimental consequence of toxicity remains unanswered. Oxygen consumption rate (OCR) and glycolysis provide sensitive and informative measures of the functional status MT and the cells metabolic regulation, yet these measures differ depending on the sample source; species, tissue type, age at measurement, and whether MT are measured in purified form or in a cell. The effects of these various parameters are difficult to quantify and not fully understood, but clearly have an impact on interpreting the bioenergetics of MT or their failure in disease states. A major goal of the review is to discuss issues and coalesce detailed information into a reference table to help in assessing mitochondrial dysfunction as a cause or consequence of Huntington's disease.
• Bioblast editor: Gnaiger E
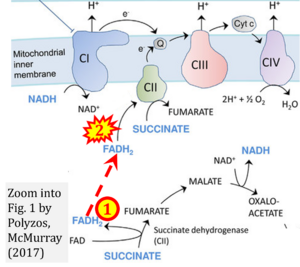
Correction: FADH2 and Complex II
- FADH2 is shown as the substrate feeding electrons into Complex II (CII). This is wrong and requires correction - for details see Gnaiger (2024).
- Gnaiger E (2024) Complex II ambiguities ― FADH2 in the electron transfer system. J Biol Chem 300:105470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105470 - »Bioblast link«
Labels:
Pathology: Neurodegenerative
Pathway: S