Ma 2012 Exp Diabetes Res: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "{{Publication |title=Ma ZA, Zhao Z, Turk J (2012) Mitochondrial dysfunction and β-cell failure in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Exp Diabetes Res 2012:703538. https://doi.org/10.1...") |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
|editor=Gnaiger E | |editor=Gnaiger E | ||
}} | }} | ||
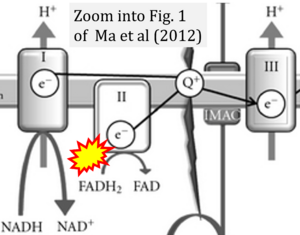
[[File:Ma 2012 Exp Diabetes Res CORRECTION.png|right|300px]] | |||
{{Template:Correction FADH2 and S-pathway}} | |||
{{Labeling | {{Labeling | ||
|diseases=Diabetes | |diseases=Diabetes | ||
}} | }} | ||
Latest revision as of 05:50, 5 November 2023
| Ma ZA, Zhao Z, Turk J (2012) Mitochondrial dysfunction and β-cell failure in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Exp Diabetes Res 2012:703538. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/703538 |
Ma ZA, Zhao Z, Turk J (2012) Exp Diabetes Res
Abstract: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is the most common human endocrine disease and is characterized by peripheral insulin resistance and pancreatic islet β-cell failure. Accumulating evidence indicates that mitochondrial dysfunction is a central contributor to β-cell failure in the evolution of T2DM. As reviewed elsewhere, reactive oxygen species (ROS) produced by β-cell mitochondria as a result of metabolic stress activate several stress-response pathways. This paper focuses on mechanisms whereby ROS affect mitochondrial structure and function and lead to β-cell failure. ROS activate UCP2, which results in proton leak across the mitochondrial inner membrane, and this leads to reduced β-cell ATP synthesis and content, which is a critical parameter in regulating glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. In addition, ROS oxidize polyunsaturated fatty acids in mitochondrial cardiolipin and other phospholipids, and this impairs membrane integrity and leads to cytochrome c release into cytosol and apoptosis. Group VIA phospholipase A₂ (iPLA₂β) appears to be a component of a mechanism for repairing mitochondrial phospholipids that contain oxidized fatty acid substituents, and genetic or acquired iPLA₂β-deficiency increases β-cell mitochondrial susceptibility to injury from ROS and predisposes to developing T2DM. Interventions that attenuate ROS effects on β-cell mitochondrial phospholipids might prevent or retard development of T2DM.
• Bioblast editor: Gnaiger E
Correction: FADH2 and Complex II
- FADH2 is shown as the substrate feeding electrons into Complex II (CII). This is wrong and requires correction - for details see Gnaiger (2024).
- Gnaiger E (2024) Complex II ambiguities ― FADH2 in the electron transfer system. J Biol Chem 300:105470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105470 - »Bioblast link«
Labels: Pathology: Diabetes