Difference between revisions of "Coupling-control state"
Beno Marija (talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{MitoPedia | {{MitoPedia | ||
|abbr=''CCS'' | |abbr=''CCS'' | ||
|description='''Coupling control states''' are defined in [[mitochondrial preparations]] (isolated mitochondria, permeabilized cells, permeabilized tissues, homogenates) as [[LEAK]], [[OXPHOS]], and [[ | |description='''Coupling control states''' are defined in [[mitochondrial preparations]] (isolated mitochondria, permeabilized cells, permeabilized tissues, homogenates) as [[LEAK]], [[OXPHOS]], and [[ET-pathway]] states of respiration (''L, P, E'') in any [[pathway control state]] which is competent for electron transfer. These coupling states are induced by application of specific inhibitors of the [[phosphorylation system]], titration of ADP and uncouplers. In intact cells, the coupling control states are [[LEAK]], [[ROUTINE]], and [[ET-pathway]] states of respiration (''L, R, E''). [[Coupling control protocol]]s induce these coupling control states sequentially at a constant [[Electron transfer-pathway state]]. | ||
|info=[[Gnaiger 2009 Int J Biochem Cell Biol]] | |info=[[Gnaiger 2009 Int J Biochem Cell Biol]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
}} | }} | ||
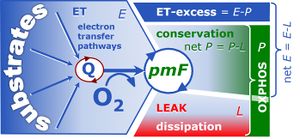
[[File:EPL-free and excess.jpg|right|300px|thumb|[[Gnaiger 2014 MitoPathways |The Blue Book 2014: Fig. 2.4.]]]] | [[File:EPL-free and excess.jpg|right|300px|thumb|[[Gnaiger 2014 MitoPathways |The Blue Book 2014: Fig. 2.4.]]]] | ||
'''Coupling control states:''' [[Image:P.jpg|link=OXPHOS capacity|OXPHOS]] [[Image:R.jpg|link=ROUTINE respiration|ROUTINE]] [[Image:E.jpg|link=ETS capacity| | '''Coupling control states:''' [[Image:P.jpg|link=OXPHOS capacity|OXPHOS]] [[Image:R.jpg|link=ROUTINE respiration|ROUTINE]] [[Image:E.jpg|link=ETS capacity|ET capacity]] [[Image:L.jpg|link=LEAK respiration|LEAK]] - [[Image:ROX.jpg|link=Residual oxygen consumption|ROX]] | ||
Communicated by [[Gnaiger E]] 2011-02-25, edited 2016-10-20. | Communicated by [[Gnaiger E]] 2011-02-25, edited 2016-10-20. | ||
Revision as of 10:04, 20 October 2017
Description
Coupling control states are defined in mitochondrial preparations (isolated mitochondria, permeabilized cells, permeabilized tissues, homogenates) as LEAK, OXPHOS, and ET-pathway states of respiration (L, P, E) in any pathway control state which is competent for electron transfer. These coupling states are induced by application of specific inhibitors of the phosphorylation system, titration of ADP and uncouplers. In intact cells, the coupling control states are LEAK, ROUTINE, and ET-pathway states of respiration (L, R, E). Coupling control protocols induce these coupling control states sequentially at a constant Electron transfer-pathway state.
Abbreviation: CCS
Reference: Gnaiger 2009 Int J Biochem Cell Biol
MitoPedia concepts:
MiP concept,
Respiratory state,
SUIT concept,
SUIT state,
Recommended
MitoPedia methods:
Respirometry
MitoPedia topics:
EAGLE
Communicated by Gnaiger E 2011-02-25, edited 2016-10-20.