Meter: Difference between revisions
From Bioblast
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Keywords SI base units}} | {{Keywords: SI base units}} | ||
{{MitoPedia concepts | {{MitoPedia concepts | ||
|mitopedia concept=Ergodynamics | |mitopedia concept=Ergodynamics | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 23:44, 17 February 2020
Description
The meter, symbol m, is the SI unit of length. It is defined by taking the fixed numerical value of the speed of light in vacuum c to be 299 792 458 when expressed in the unit m s−1, where the second is defined in terms of the caesium frequency ΔνCs.
Abbreviation: m
Reference: Bureau International des Poids et Mesures (2019) The International System of Units (SI). 9th edition:117-216 ISBN 978-92-822-2272-0. - »Open Access pdf«
- Bioblast links: SI base units - >>>>>>> - Click on [Expand] or [Collapse] - >>>>>>>
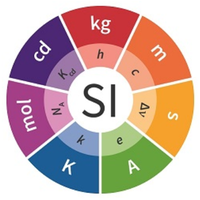
- Entity, count, and number, and SI base quantities / SI base units
Quantity name Symbol Unit name Symbol Comment elementary UX elementary unit [x] UX, UB; [x] not in SI count NX elementary unit [x] NX, NB; [x] not in SI number N - dimensionless = NX·UX-1 amount of substance nB mole [mol] nX, nB electric current I ampere [A] A = C·s-1 time t second [s] length l meter [m] SI: metre mass m kilogram [kg] thermodynamic temperature T kelvin [K] luminous intensity IV candela [cd]
- Fundamental relationships
- » Avogadro constant NA
- » Boltzmann constant k
- » elementary charge e
- » Faraday constant F
- » gas constant R
- » electrochemical constant f
- Fundamental relationships
- SI and related concepts
MitoPedia concepts:
Ergodynamics