Semantic search
| Term | Abbreviation | Description |
|---|---|---|
| SUIT-031 Q mt D072 | PM+S+Rot | 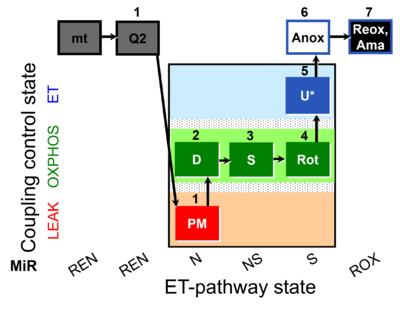 |
| SUITbrowser | Use the SUITbrowser to find the substrate-uncoupler-inhibitor-titration (SUIT) protocol most suitable for addressing your research questions. Open the SUITbrowser: http://suitbrowser.oroboros.at/ | |
| Select O2k - DatLab | Select O2k - DatLab | |
| Selectivity | Selectivity is the ability of a sensor or method to quantify accurately and specifically the analyte or analytes in the presence of other compounds. | |
| Sensitivity | Sensitivity refers to the response obtained for a given amount of analyte and is often denoted by two factors: the limit of detection and the limit of quantification. | |
| Smoothing | Various methods of smoothing can be applied to improve the signal-to-noise ratio. For instance, data points recorded over time [s] or over a range of wavelengths [nm] can be smoothed by averaging n data points per interval. Then the average of the n points per smoothing interval can be taken for each successively recorded data point across the time range or range of the spectrum to give a n-point moving average smoothing. This method decreases the noise of the signal, but clearly reduces the time or wavelength resolution. More advanced methods of smoothing are applied to retain a higher time resolution or wavelength resolution. | |
| Stability | Stability determines the accuracy of intensity and absorbance measurements as a function of time. Instability (see drift introduces systematic errors in the accuracy of fluorescence and absorbance measurements. | |
| Startup O2k-Respirometer | Startup O2k-Respirometer - the experimental system complete for basic high-resolution respirometry (HRR). The O2k-Respirometer includes the O2k-Main Unit with stainless steel housing, O2k-Assembly Kit, two OroboPOS (polarographic oxygen sensors) and OroboPOS-Service Kit, DatLab software, the ISS-Integrated Suction System, the O2k-Titration Set, and for performing high-resolution respirometry with reduced amounts of biological sample the O2k-sV-Module.
| |
| Steady state | A system is in a steady state if the state variables of a dynamic system do not change over time due to exchange processes with the environment, which compensate for internal dissipative transformations — such as chemical reactions or diffusion — and thus prevent any changes of the system and externalize dissipative changes to the environment. The dynamic nature of the steady state differentiates it from the thermodynamic equilibrium state. {Quote} Steady states can be obtained only in open systems, in which changes by internal transformations, e.g., O2 consumption, are instantaneously compensated for by external fluxes across the system boundary, e.g., O2 supply, thus preventing a change of O2 concentration in the system (Gnaiger 1993). Mitochondrial respiratory states monitored in closed systems satisfy the criteria of pseudo-steady states for limited periods of time, when changes in the system (concentrations of O2, fuel substrates, ADP, Pi, H+) do not exert significant effects on metabolic fluxes (respiration, phosphorylation). Such pseudo-steady states require respiratory media with sufficient buffering capacity and substrates maintained at kinetically-saturating concentrations, and thus depend on the kinetics of the processes under investigation. {end of Quote: BEC 2020.1}. Whereas fluxes may change at a steady state over time, concentrations are maintained constant. The 'respiratory steady state' (Chance and Williams 1955) is characterized by constant fluxes (O2 flux, H2O2 flux) and measured variables of state (cytochrome redox states, Q redox state, NADH redox state, mitochondrial membrane potential). High-resolution respirometry allows for the measurement of several parameters (e.g. O2 flux, H2O2 flux, mitochondrial membrane potential) at pseudo-steady states, when changes of concentrations in the closed system do not exert any control on fluxes. Combination with the Titration-Injection microPump (TIP2k) allows operation with programmable titration regimes at steady-state ADP concentration (Gnaiger 2001), oxygen concentration (oxystat mode; Gnaiger et al 2000, Harrison et al 2015) or steady-state pH (pH-stat more), yielding an expanded flexibility in experimental design by combining the technical advantages of closed and open systems approaches. | |
| Substrate control state | See Electron-transfer-pathway state | |
| Substrate-uncoupler-inhibitor titration | SUIT | Mitochondrial Substrate-uncoupler-inhibitor titration (SUIT) protocols are used with mitochondrial preparations to study respiratory control in a sequence of coupling and substrates states induced by multiple titrations within a single experimental assay. |
| TIP2k-Module | TIP2k-Module - Titration-Injection microPump (TIP2k) for two-channel operation with the O2k-FluoRespirometer with automatic control by DatLab of programmable titration regimes and feedback control (oxystat, pH-stat). | |
| TPP+ inhibitory effect | A major task in establishing a procedure for measurement of mitochondrial membrane potential using probe molecules is the evaluation of inhibitory concentrations of the probe molecule on the activity of respiration. The TPP+ inhibitory effect (this also applies to TPMP+ and other indicator molecules) is frequently ignored. Accurate knowledge of a threshold concentration is required to evaluate the necessary limit of detection of TPP+, and for restriction of experimental TPP+ concentrations below the inhibitory range. | |
| Taurine | Taurine, or 2-Aminoethan sulfonic acid, is one of the most abundant low-molecular-weight organic constituents in animals and humans. It has a multitude of functions in different types of tissue, one of which is the stabilization of membranes. Because of this and its antioxidative effect, taurine is a component of the respiration media MiR05 and MiR06 to preserve mitochondrial function. | |
| Tetraphenylphosphonium | TPP+ | Tetraphenylphosphonium (TPP+). A lipophilic molecular probe in conjunction with an ion selective electrode (ISE) for measuring the mitochondrial membrane potential. |
| Time resolution | Time resolution in respirometric measurements is influenced by three parameters: the response time of the POS, the data sampling interval and the number of points used for flux calculation. | |
| Uncoupler titrations | In uncoupler titrations various uncouplers, such as CCCP, FCCP or DNP are applied to uncouple mitochondrial electron transfer from phosphorylation (ATP synthase, ANT and phosphate carrier), particularly with the aim to measure ET capacity. ET capacity is maximum oxygen flux measured as noncoupled respiration with optimum uncoupler concentration. | |
| Uncoupling-control ratio | UCR | The uncoupling-control ratio UCR is the ratio of ET-pathway/ROUTINE-respiration (E/R) in living cells, evaluated by careful uncoupler titrations (Steinlechner et al 1996). Compare ROUTINE-control ratio (R/E) (Gnaiger 2008). |
| Unspecific binding of TPP+ | Unspecific binding of the probe molecule TPP+ in the matrix phase of mitochondria is taken into account as a correction for measurement of the mitochondrial membrane potential. External unspecific binding is the binding outside of the inner mt-membrane or on the outer side of the inner mt-membrane, in contrast to internal unspecific binding. | |
| VO2max | VO2max; VO2max/M | Maximum oxygen consumption, VO2max, is and index of cardiorespiratory fitness, measured by spiroergometry on human and animal organisms capable of controlled physical exercise performance on a treadmill or cycle ergometer. VO2max is the maximum respiration of an organism, expressed as the volume of O2 at STPD consumed per unit of time per individual object [mL.min-1.x-1]. If normalized per body mass of the individual object, M [kg.x-1], mass specific maximum oxygen consumption, VO2max/M, is expressed in units [mL.min-1.kg-1]. |
| Warburg effect | Recently, controversies had a renaissance on the much neglected Crabtree effect (aerobic glycolysis in a large range of cells exposed to glucose or fructose, with fully functional mitochondria; Crabtree 1929; Gnaiger and Kemp 1990) versus the Warburg effect (loss of mitochondrial function inducing cancer and stimulating compensatory aerobic glycolysis in the presence of oxygen; Warburg 1956; see list of references for reviews). Today it is widely accepted that ‘the Warburg effect is not consistent across all cancer types’ (Potter et al 2016) and reprogramming of mitochondrial energy metabolism represents a functional adjustment of cancer cells (Schöpf et al 2020). | |
| Zero calibration | R0 | Zero calibration is, together with air calibration, one of the two steps of the POS calibration. It is performed in the closed chamber after all the oxygen has been depleted by the addition of dithionite or by respiration of imt or cells. Any incubation medium can be used for zero calibration with dithionite or sample. Unlike air calibration, it is not necessary to perform a zero calibration on each experimental day. After performing a zero calibration, it is recommended not running other experiments on the same day. Even after standard cleaning of the O2k-chambers, there might be residual amounts of reduced dithionite in the chamber, affecting the oxygen flux in subsequent experiments performed on the same day. |


