Gopan 2021 World J Hepatol
| Gopan A, Sarma MS (2021) Mitochondrial hepatopathy: Respiratory chain disorders- 'breathing in and out of the liver'. World J Hepatol 13:1707-26. https://doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v13.i11.1707 |
Gopan A, Sarma MS (2021) World J Hepatol
Abstract: Mitochondria, the powerhouse of a cell, are closely linked to the pathophysiology of various common as well as not so uncommon disorders of the liver and beyond. Evolution supports a prokaryotic descent, and, unsurprisingly, the organelle is worthy of being labeled an organism in itself. Since highly metabolically active organs require a continuous feed of energy, any dysfunction in the structure and function of mitochondria can have variable impact, with the worse end of the spectrum producing catastrophic consequences with a multisystem predisposition. Though categorized a hepatopathy, mitochondrial respiratory chain defects are not limited to the liver in time and space. The liver involvement is also variable in clinical presentation as well as in age of onset, from acute liver failure, cholestasis, or chronic liver disease. Other organs like eye, muscle, central and peripheral nervous system, gastrointestinal tract, hematological, endocrine, and renal systems are also variably involved. Diagnosis hinges on recognition of subtle clinical clues, screening metabolic investigations, evaluation of the extra-hepatic involvement, and role of genetics and tissue diagnosis. Treatment is aimed at both circumventing the acute metabolic crisis and long-term management including nutritional rehabilitation. This review lists and discusses the burden of mitochondrial respiratory chain defects, including various settings when to suspect, their evolution with time, including certain specific disorders, their tiered evaluation with diagnostic algorithms, management dilemmas, role of liver transplantation, and the future research tools.
• Bioblast editor: Gnaiger E
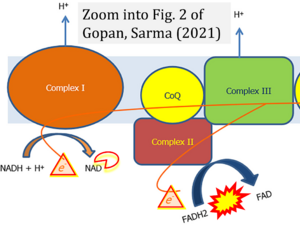
Correction: FADH2 and Complex II
- FADH2 is shown as the substrate feeding electrons into Complex II (CII). This is wrong and requires correction - for details see Gnaiger (2024).
- Gnaiger E (2024) Complex II ambiguities ― FADH2 in the electron transfer system. J Biol Chem 300:105470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105470 - »Bioblast link«
Hydrogen ion ambiguities in the electron transfer system
Communicated by Gnaiger E (2023-10-08) last update 2023-11-10
- Electron (e-) transfer linked to hydrogen ion (hydron; H+) transfer is a fundamental concept in the field of bioenergetics, critical for understanding redox-coupled energy transformations.
- However, the current literature contains inconsistencies regarding H+ formation on the negative side of bioenergetic membranes, such as the matrix side of the mitochondrial inner membrane, when NADH is oxidized during oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS). Ambiguities arise when examining the oxidation of NADH by respiratory Complex I or succinate by Complex II.
- Oxidation of NADH or succinate involves a two-electron transfer of 2{H++e-} to FMN or FAD, respectively. Figures indicating a single electron e- transferred from NADH or succinate lack accuracy.
- The oxidized NAD+ is distinguished from NAD indicating nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide independent of oxidation state.
- NADH + H+ → NAD+ +2{H++e-} is the oxidation half-reaction in this H+-linked electron transfer represented as 2{H++e-} (Gnaiger 2023). Putative H+ formation shown as NADH → NAD+ + H+ conflicts with chemiosmotic coupling stoichiometries between H+ translocation across the coupling membrane and electron transfer to oxygen. Ensuring clarity in this complex field is imperative to tackle the apparent ambiguity crisis and prevent confusion, particularly in light of the increasing number of interdisciplinary publications on bioenergetics concerning diagnostic and clinical applications of OXPHOS analysis.