Yang 2022 Front Cell Dev Biol
| Yang J, Guo Q, Feng X, Liu Y, Zhou Y (2022) Mitochondrial dysfunction in cardiovascular diseases: potential targets for treatment. Front Cell Dev Biol 10:841523. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2022.841523 |
Yang J, Guo Q, Feng X, Liu Y, Zhou Y (2022) Front Cell Dev Biol
Abstract: Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are serious public health issues and are responsible for nearly one-third of global deaths. Mitochondrial dysfunction is accountable for the development of most CVDs. Mitochondria produce adenosine triphosphate through oxidative phosphorylation and inevitably generate reactive oxygen species (ROS). Excessive ROS causes mitochondrial dysfunction and cell death. Mitochondria can protect against these damages via the regulation of mitochondrial homeostasis. In recent years, mitochondria-targeted therapy for CVDs has attracted increasing attention. Various studies have confirmed that clinical drugs (β-blockers, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors/angiotensin receptor-II blockers) against CVDs have mitochondrial protective functions. An increasing number of cardiac mitochondrial targets have shown their cardioprotective effects in experimental and clinical studies. Here, we briefly introduce the mechanisms of mitochondrial dysfunction and summarize the progression of mitochondrial targets against CVDs, which may provide ideas for experimental studies and clinical trials.
• Bioblast editor: Gnaiger E
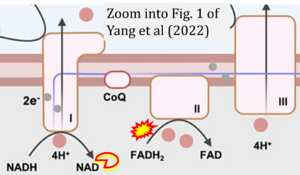
Correction: FADH2 and Complex II
- FADH2 is shown as the substrate feeding electrons into Complex II (CII). This is wrong and requires correction - for details see Gnaiger (2024).
- Gnaiger E (2024) Complex II ambiguities ― FADH2 in the electron transfer system. J Biol Chem 300:105470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105470 - »Bioblast link«
Hydrogen ion ambiguities in the electron transfer system
Communicated by Gnaiger E (2023-10-08) last update 2023-11-10
- Electron (e-) transfer linked to hydrogen ion (hydron; H+) transfer is a fundamental concept in the field of bioenergetics, critical for understanding redox-coupled energy transformations.
- However, the current literature contains inconsistencies regarding H+ formation on the negative side of bioenergetic membranes, such as the matrix side of the mitochondrial inner membrane, when NADH is oxidized during oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS). Ambiguities arise when examining the oxidation of NADH by respiratory Complex I or succinate by Complex II.
- Oxidation of NADH or succinate involves a two-electron transfer of 2{H++e-} to FMN or FAD, respectively. Figures indicating a single electron e- transferred from NADH or succinate lack accuracy.
- The oxidized NAD+ is distinguished from NAD indicating nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide independent of oxidation state.
- NADH + H+ → NAD+ +2{H++e-} is the oxidation half-reaction in this H+-linked electron transfer represented as 2{H++e-} (Gnaiger 2023). Putative H+ formation shown as NADH → NAD+ + H+ conflicts with chemiosmotic coupling stoichiometries between H+ translocation across the coupling membrane and electron transfer to oxygen. Ensuring clarity in this complex field is imperative to tackle the apparent ambiguity crisis and prevent confusion, particularly in light of the increasing number of interdisciplinary publications on bioenergetics concerning diagnostic and clinical applications of OXPHOS analysis.
Labels: Pathology: Cardiovascular